Pressure of solids problems and solutions. It differs from the mass because it is.
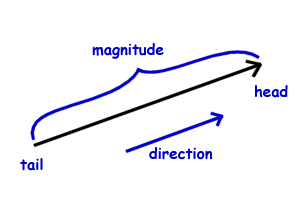
Examples of Vector Quantities.
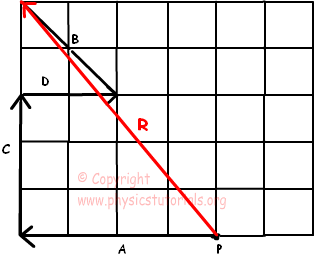
Vector examples in physics. Vector quantity examples are many some of them are given below. If vector B represents 100 m of displacement north find the addition of the two displacements R. - The laws of physics are independent of the choice of coordinate system.
For example for the vector A we would write. Vectors Physics-The relationships among vectors do not depend on the location of the origin of the coordinate system or on the orientation of the axes. For example many of you say that the velocity of a particle is five.
Easy Vector A represents 50 m of displacement east. Simply put vectors are those physical quantities that have values as well as specific directions. We often use a position vector vec rt to describe the position of an object as a function of time.
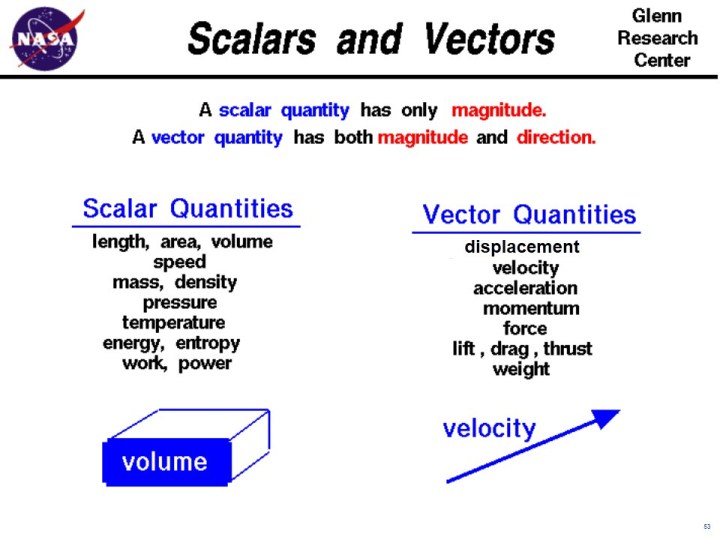
Such as displacement velocity etc. Vectors are one of the most. In other words scalar quantity has magnitude such as size or length but no particular direction.
Vector Addition using and html5 applet to understand the geometrical meaning of the addition of vectors important. Vectors Click here to see the solutions. In National 5 Physics learn how add two vectors to find their resultant.
Likewise for y and z. Since velocity is a vector. That is .
For example velocity is a vector with speed and direction. Several answers already defined a vector quantity as having a magnitude how big and direction where. Free SAT II Physics Practice Questions Vectors with detailed solutions and explanations.
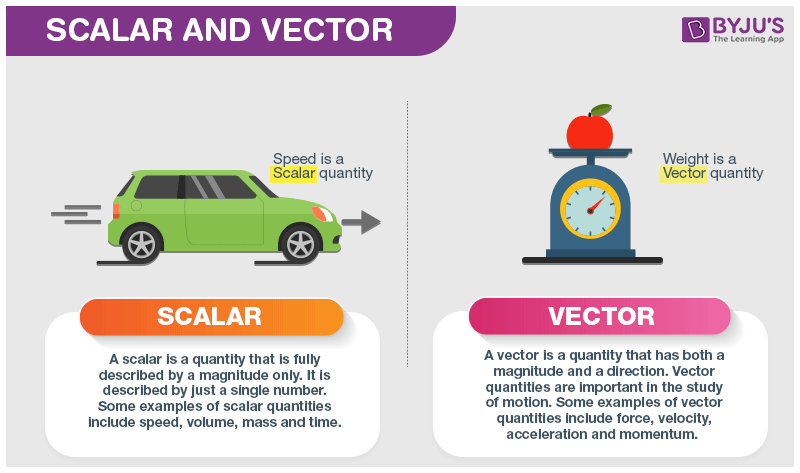
Introduction to Vector in Physics. Here we have defined both these quantities and created a list containing examples of both vector and scalar quantities. This is oposed to a scalar quantity which has only a magnitude but no.
A vector with the value of magnitude equal to one and direction is called unit vector represented by a lowercase alphabet with a hat circumflex. Classify physical quantities into scalars or vectors. In this article you will also get to know the differences and some similarities between both scalar and vector quantities.
When it does have a particular direction its a vector quantity. The resultant of two vectors. For example displacement velocity and acceleration are vector quantities while speed the magnitude of velocity time and mass are scalars.
17 - Calculating Vector Components in Physics Part 1 Component form of a Vector - YouTube. Any vector can be expressed as a sum of multiples of these basic vectors. The weight is a magnitude that expresses the force exerted by an object on a point of support as a consequence of the local gravitational attraction.
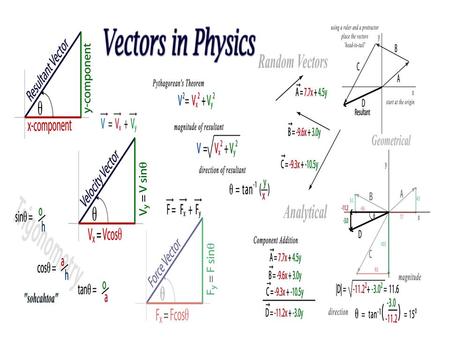
Ax x For example consider the vector shown in Figure 36 a. One of these is vector addition written symbolically as A B C vectors are conventionally written as boldface. Here we would say that Ax is the x component of the vector A.
This article about vectors and scalars in physics gives a basic introduction of both these quantities. It is represented vectorially from the center of gravity of the object and towards the center of the Earth or from the object generating gravity. There are diverse examples for vector quantity such as momentum linear momentum acceleration displacement angular velocity force etc.
Because the object can move the position vector is a function of time. Two children A and B push a block if A push the block southward with force of 400 N and at the same time B push the block eastward with force of 300 N then determine the resultant of. We use vectors to represent certain quantities with magnitude and direction.
All these have designated directions in which they workperformoccur. Vector Direction and Bearing With examples applications and questions with solutions. In this case Ax 7 0 O and Ay 6 0 as indicated in the figure.
For example Newtons Laws are a mathematical framework that introduce the concepts of force and mass in order to model and determine how an object will move through space. Addition of vectors by components in two dimensions. Similarly the signs of Ax and Ay are given Ax 0 in Figures 36 b c d for the vectors shown there.
Interactive Html 5 applets to add and subtract vectors. Parallel and Perpendicular Vectors with questions some of. Vector is a measurement that refers to both the magnitude of the unit and the direction of the movement the unit has taken.
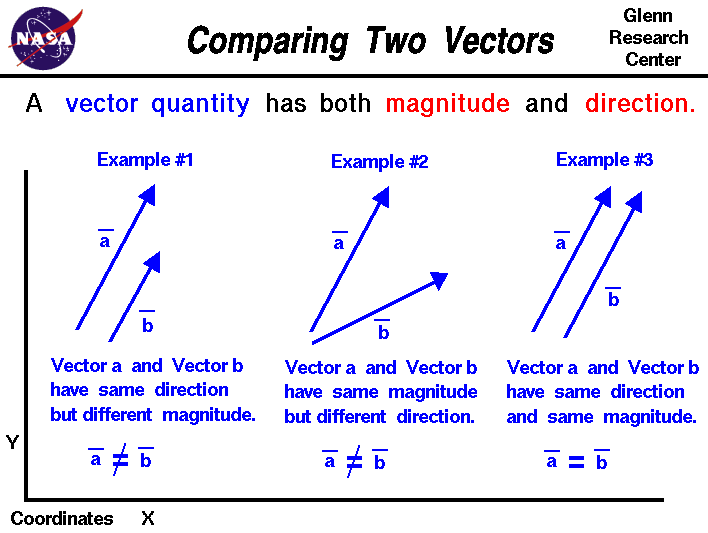
To qualify as a vector a quantity having magnitude and direction must also obey certain rules of combination. That is you need to describe the direction of the quantity with the measurable properties of the physical quantity here. Some other common physics examples of a vector are velocityms and forceN.
38 2 2 2 2 a a x a y a x a y Multiplying vectors-Vector by a scalar-Vector by a vector. Easy Determine the x and y components of a displacement whose magnitude is 300 m at a 23 angle from the x-axis. A AxiAyjAzk.
Examples of vector quantities. Addition and Subtraction of Vectors with examples Scalar Product of Vectors with questions some of which may be challenging that explains the application of the scalar product.

Vectors Scalars Physics 11 Vectors Scalars A Vector Has Magnitude As Well As Direction Examples Displacement Velocity Acceleration Force Momentum Ppt Download

2 1 Scalars And Vectors University Physics Volume 1
Vectors Vector A Quantity That Has Both Magnitude Size And Direction Examples Displacement Velocity Acceleration Scalar A Quantity That Has No Ppt Download
Physics4kids Com Motion Vectors

Vector Definition Physics Facts Britannica

Examples Of Vector And Scalar Quantity In Physics
Physics For Kids Scalars And Vectors
Vector And Scalar Definition Vector Addition And Subtraction Differences Solved Problems

Scalar Function Definition Of Scalar Calculus How To

2 1 Scalars And Vectors University Physics Volume 1

Vector Definition Physics Facts Britannica


Post a Comment
Post a Comment